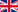
The skin serves as an envelope that separates an individual from the outside world. This organ protects against various external influences. It is composed of three parts. The topmost (or outermost) part is formed by the epidermis. Underneath lies the dermis, or the corium. These layers largely form the skin. The bottom part is the subcutaneous connective tissue, the so-called subcutis (connective tissue serves to connect and support other tissues and organs). Below the subcutis is the layer of fat. The skin also includes appendages: sebaceous glands, sweat glands, hair roots, areas where nails are formed, and the nail bed.
Skin Problems and Probiotics
A skin problem, such as eczema, for instance, often surfaces when your immune system is weakened. To support this natural resistance, it is wise to use probiotics. Probiotics are living bacteria, like certain lactic acid bacteria, which when taken in sufficient quantities, contribute to a healthy gut flora (all good and bad bacteria in the intestine), thus supporting the natural immunity. The gut flora is considered healthy when there are more good bacteria than bad ones. By consuming probiotics, the amount of good bacteria is supplemented.
What is Atopic Eczema?
Atopic eczema, also called constitutional eczema, is a common skin condition that is part of the atopy syndrome. In this syndrome, inflammatory reactions occur in the body due to a predisposition to overreact to substances or stimuli from the environment. These inflammatory reactions can manifest in the skin as atopic eczema, in the mucous membranes of the nose and eyes as hay fever, and in the airways as asthma. This predisposition is genetic and can essentially manifest at any age, but usually shortly after birth.
How Does Atopic Eczema Develop?
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown. It is believed that eczema occurs due to a combination of various factors. First, there is a genetic predisposition. Additionally, there are influences of allergic and non-allergic factors from the environment. These factors can affect the skin both externally and internally.
Non-allergic factors include water, soap, dry air, heat, perspiration, and woolen clothing. Infections by bacteria and viruses can also exacerbate eczema. Stress, both physical and psychological, can lower the skin's threshold for stimuli, which can worsen eczema. An allergy to food or inhaled substances (inhalation allergens) can potentially play a role in the course of atopic eczema. Examples of foods that can cause allergies are cow's milk, chicken egg, peanuts, and nuts. Examples of inhalation allergens are house dust mites, animal dander, and pollen from grasses and trees.
Need more information or want to make an appointment?
Book an appointment online at one of our locations, or call 085 - 0655499. If you have questions about acupuncture or how acupuncture can help you, you can also contact us via email.
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake A session in which we discuss your complaints and propose a treatment plan
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Intake
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment Choose a location and schedule your desired treatment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
Appointment
Choose your location / acupuncturist:
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of atopic eczema include redness and flaking of the skin, the appearance of small bumps and sometimes fluid-filled blisters. There may also be fluid secretion. Since eczema causes itching, scratching effects are often present. Scratching and rubbing contribute to the maintenance of eczema. If eczema persists for a long time, the skin becomes rough.
Atopic eczema usually develops in the first 6 months of life, but can essentially start at any age. The course is very variable, with better and worse periods. The eczema can be present for a relatively short time but can also become chronic. In some people, it disappears only to return much later.
Hay Fever
Related to the above conditions is also the (seasonal) hay fever.
Effectiveness of Acupuncture
For allergies and skin conditions, acupuncture has proven to be effective. Often, redness, swelling, and itching disappear during the course of a few treatments. It is important to discuss with your acupuncturist how to prevent recurrence of the allergy or skin condition.